Building an Unforgettable Brand
A strong corporate brand is essential for success. This listicle provides eight key corporate branding strategies to elevate your brand and achieve lasting impact. Whether you’re a Fortune 100 company or a tech startup, learn how to build a memorable brand experience using these strategies: Brand Architecture, Brand Positioning, Purpose-Driven Branding, Employer Branding, Digital-First Branding, Co-Branding, Storytelling, and Experiential Branding. These powerful corporate branding strategies can transform your business, differentiating you from competitors and building lasting customer loyalty.
1. Brand Architecture Strategy
A robust brand architecture strategy is arguably the most crucial element of any successful corporate branding initiative. It provides the blueprint for how a company structures, manages, and presents its various brands to the market. Essentially, it defines the hierarchy, relationships, and roles of different brands within a corporation's portfolio. This clarity helps stakeholders, from internal teams to investors and customers, understand how various products and services relate to the parent company and to each other. This strategic approach is essential for companies looking to maximize brand equity and streamline their marketing efforts, making it a foundational element of corporate branding strategies.
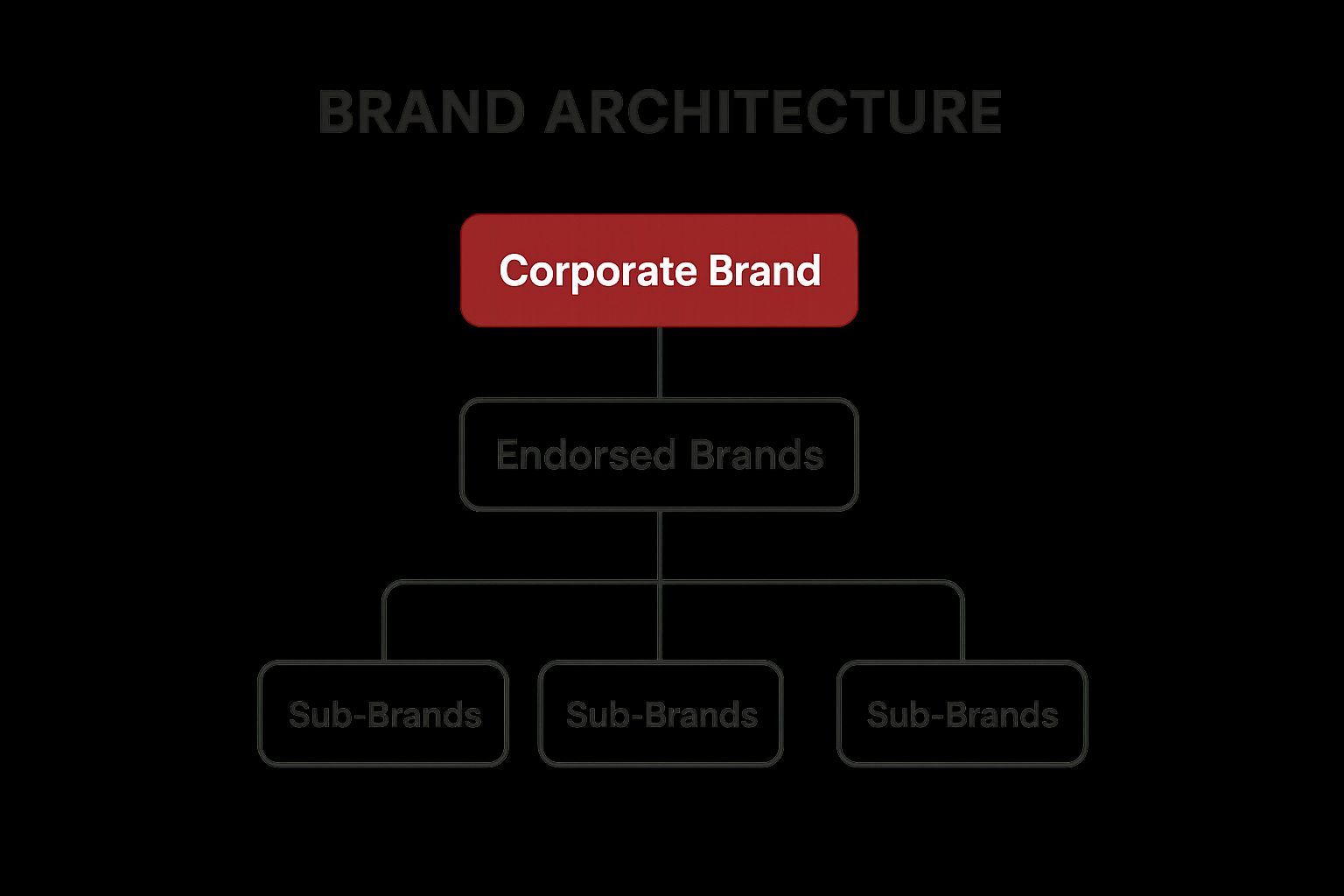
This infographic visually represents the hierarchical relationship between different branding models. At the top, we see the overarching concept of "Brand Architecture," which encompasses all the strategies below. The primary levels beneath this are "Monolithic," "Endorsed," and "Hybrid," each representing a different approach to structuring a brand portfolio. Within "Endorsed," we see sub-categories like "Strong Endorsement" and "Weak Endorsement," demonstrating the varying degrees of connection between parent and sub-brands. Finally, examples of companies employing each model illustrate real-world applications of these strategic choices. The infographic highlights the importance of choosing the right model based on company structure and marketing objectives.
Brand architecture encompasses key features such as defining hierarchical relationships between corporate, parent, and sub-brands; establishing visual and verbal identity guidelines; creating a strategic framework for brand portfolio management; and determining how new acquisitions and products are branded. For example, a company might decide on a "branded house" strategy like FedEx, where all services fall under the FedEx umbrella, creating a unified and easily recognizable brand identity. Conversely, a "house of brands" strategy, like that of Procter & Gamble, allows individual product brands like Tide and Pampers to cultivate distinct identities and appeal to specific market segments.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Implementing a well-defined brand architecture is particularly critical for companies with complex portfolios, multiple product lines, or those undergoing mergers and acquisitions. It provides a roadmap for navigating the intricacies of multi-brand management, ensuring consistency and synergy across all touchpoints. This approach also helps in leveraging brand equity across products, facilitating more efficient marketing resource allocation, and clarifying brand relationships for customers and stakeholders.
Pros:
- Provides clarity for customers and stakeholders about brand relationships
- Enables strategic leveraging of brand equity across products
- Facilitates more efficient marketing resource allocation
- Helps navigate complex multi-brand businesses
Cons:
- Complex to implement across large organizations
- Requires significant resource investment to maintain consistency
- Can be challenging to adjust when market conditions change
- May limit flexibility for individual brands
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Procter & Gamble: Employs a "House of Brands" strategy with distinct brands like Tide, Pampers, and Gillette.
- FedEx: Utilizes a "Branded House" approach with FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, and FedEx Freight under consistent master branding.
- Virgin Group: Demonstrates an endorsed brand architecture with Virgin Atlantic, Virgin Mobile, etc.
- Alphabet Inc.: Restructured Google and its subsidiaries to create a clearer brand architecture.
Actionable Tips:
- Audit: Conduct a thorough audit of current brand relationships before developing architecture.
- Future-Proofing: Consider future growth and potential acquisitions.
- Alignment: Ensure architecture supports overall business objectives.
- Clarity: Create clear brand relationship guidelines for implementation.
- Review: Regularly review and update the architecture as the business evolves.
This structured approach to branding is crucial for Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, corporate marketing teams, venture capital firms, and even event coordinators. By investing in a clear and well-defined brand architecture, organizations can ensure consistency, maximize brand equity, and navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace. This strategy deserves its place at the top of the list of corporate branding strategies because it lays the foundation for all other branding efforts. A well-defined architecture ensures that every branding activity, from logo design to marketing campaigns, contributes to a cohesive and impactful brand experience.
2. Brand Positioning Strategy
Brand positioning is a crucial element of any successful corporate branding strategy. It defines how your company differentiates itself in the minds of target customers compared to competitors. It's not just about what you sell, but why customers should choose you over the alternatives. A strong brand position articulates your unique value proposition, establishes what your brand stands for, its core benefits, and the specific needs it fulfills for your target audience. Effective brand positioning carves out a distinctive space for your company in the market, influencing customer perceptions and driving purchase decisions.

This strategy works by identifying specific target audience segments and tailoring the brand message to resonate with their needs and aspirations. It involves a deep understanding of the competitive landscape to pinpoint opportunities for differentiation. By highlighting unique features, benefits, or values, a company can establish a clear and compelling reason for customers to choose its products or services. This differentiation can be based on various factors such as product quality, innovation, customer service, price, or even brand personality.
Examples of successful brand positioning abound. Apple has consistently positioned itself as innovative, premium, and user-friendly, attracting a loyal customer base willing to pay a premium for its products. Volvo has built its reputation on safety, making it the go-to brand for safety-conscious consumers. Patagonia differentiates itself through its commitment to environmental activism, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Dollar Shave Club disrupted the razor market by positioning itself against expensive razor brands, offering a more affordable and convenient alternative.
For companies developing their corporate branding strategies, brand positioning is essential for several reasons. It provides strategic direction for all marketing activities, ensuring consistent messaging across all channels. This consistency reinforces the brand's identity and strengthens its presence in the market. A well-defined brand position also enables companies to command premium pricing, justifying higher costs with perceived value and exclusivity. Furthermore, strong positioning fosters deeper emotional connections with customers, building brand loyalty and advocacy. Learn more about Brand Positioning Strategy
Key features of a strong brand positioning strategy:
- Identifies target audience segments with precision: Understanding the specific needs, desires, and motivations of your target audience is paramount.
- Articulates a unique value proposition: This is the core of your brand positioning, explaining why customers should choose you over competitors.
- Defines the competitive frame of reference: Identifying your main competitors and understanding their positioning is crucial.
- Establishes key points of differentiation: Highlighting what makes your brand unique and superior to the competition.
- Creates a consistent messaging framework: Ensuring that your brand message is consistent across all communication channels.
Pros:
- Creates clear market differentiation
- Guides consistent communication across channels
- Helps command premium pricing
- Builds stronger emotional connections with customers
- Provides strategic direction for all marketing activities
Cons:
- Difficult to change once established
- Requires significant market research investment
- May limit expansion into new categories if too narrow
- Competitors may attempt to copy successful positioning
Tips for effective brand positioning:
- Conduct thorough competitive analysis before defining your position.
- Ensure positioning is relevant, distinctive, and credible.
- Test positioning concepts with target audiences to gauge effectiveness.
- Develop a formal positioning statement document as a reference for all marketing efforts.
- Maintain consistency while allowing for evolution to adapt to changing market dynamics.
Pioneered by marketing giants like Al Ries and Jack Trout (authors of Positioning: The Battle for Your Mind) and David Aaker (brand equity expert), and implemented successfully by brands like Nike and Coca-Cola, brand positioning is an indispensable tool for any company aiming to build a strong and enduring brand. Whether you are a Fortune 100 company, a tech startup, or an event coordinator, a well-defined brand position provides the foundation for all other branding and marketing initiatives, ensuring that your message resonates with your target audience and drives business success.
3. Purpose-Driven Branding Strategy
In today's increasingly socially conscious landscape, a purpose-driven branding strategy is a powerful approach among corporate branding strategies. This strategy centers a company's brand around a meaningful social purpose or mission that goes beyond simply generating profits. It connects the brand to larger societal issues or values that resonate with stakeholders, making the organization's reason for existence about creating a positive impact alongside business success. This approach transforms the brand from simply selling products or services to becoming a force for good in the world.

A purpose-driven branding strategy features several key components: a clearly articulated company purpose or mission statement, alignment of business operations with the stated purpose, integration of purpose into all brand touchpoints (from marketing materials to customer service interactions), a long-term commitment to relevant social or environmental causes, and authentic storytelling that showcases the impact the company is making. This strategy deserves a place on any list of top corporate branding strategies because it offers a pathway to building a more resilient and impactful brand in the modern marketplace. It allows companies to connect with customers on a deeper level, attract top talent, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Patagonia: Known for its environmental activism and commitment to "planet over profit," Patagonia actively supports environmental conservation efforts and integrates sustainable practices throughout its supply chain.
- TOMS Shoes: The original "One for One" giving model, where a pair of shoes is donated for every pair purchased, exemplified purpose-driven branding. While the model has evolved, the core commitment to social impact remains.
- Ben & Jerry's: This ice cream brand has a long history of social justice advocacy, incorporating their stances on issues like fair trade and LGBTQ+ rights into their branding and product development.
- Unilever: With its Sustainable Living Plan, Unilever has integrated sustainability across its vast brand portfolio, demonstrating how large corporations can embed purpose into their operations.
Pros:
- Builds deeper emotional connections with consumers
- Attracts and retains purpose-oriented employees
- Creates differentiation in crowded markets
- Resonates with socially-conscious consumers, especially Millennials and Gen Z
- Can generate positive publicity and earned media
Cons:
- Risk of being perceived as "purpose-washing" if not authentic
- May alienate consumers who disagree with the chosen purpose
- Requires significant operational changes to align business with purpose
- Results may take longer to materialize than traditional marketing
- Can create backlash if the company fails to live up to stated values
Tips for Implementation:
- Identify a purpose that authentically connects to your business model: Don't force a cause; find one that resonates with your core values and operations.
- Ensure leadership genuinely embraces the purpose beyond marketing: Purpose must be embedded in the company culture, not just a marketing tactic.
- Implement measurable impact initiatives tied to the purpose: Track and report on the positive change you're creating.
- Be transparent about progress and challenges: Authenticity builds trust.
- Integrate purpose into hiring, operations, and product development: Make purpose a core part of your business DNA.
Popularized By: Simon Sinek (Start With Why), Larry Fink (BlackRock CEO's annual letters on purpose), Paul Polman (former Unilever CEO), B Corporation movement
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This strategy is particularly effective for companies targeting younger demographics, those operating in highly competitive markets, and businesses looking to build long-term brand loyalty and resilience. It's crucial to remember that authenticity is key. Consumers are savvy and can spot inauthentic purpose-washing efforts quickly. A truly purpose-driven brand walks the talk, aligning its actions with its stated values, which resonates deeply with today's conscious consumers and creates lasting positive impact.
4. Employer Branding Strategy
In the competitive landscape of corporate branding strategies, employer branding has become a critical component of success, particularly for Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, and organizations seeking top talent. This strategy focuses on cultivating and promoting your company's reputation as an employer of choice. It's about articulating a unique Employee Value Proposition (EVP) – showcasing the benefits, culture, and opportunities that make your organization attractive to both current and potential employees. Effectively implemented, employer branding aligns seamlessly with your overall corporate branding but specifically targets talent markets, enhancing your ability to attract, engage, and retain the best people.
How it Works:
Employer branding operates on the principle that your employees are your most valuable asset and, simultaneously, powerful brand ambassadors. By fostering a positive and authentic internal culture, you create a ripple effect that positively impacts your external brand perception. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing:
- EVP Development: Defining what makes your company a unique and desirable place to work, encompassing compensation, benefits, career development, work-life balance, and company culture.
- Consistent Messaging: Ensuring consistent communication of your EVP both internally and externally across all channels, from career pages to social media.
- Workplace Culture Cultivation: Actively shaping and nurturing a positive and supportive work environment that aligns with your EVP.
- Candidate Experience Management: Optimizing the recruitment process to provide a positive and seamless experience for all candidates, regardless of the outcome.
- Employee Advocacy Programs: Empowering employees to share their positive experiences and become authentic brand ambassadors.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several organizations have successfully leveraged employer branding to gain a competitive edge:
- Google: Known for its exceptional workplace perks, innovative culture, and focus on employee well-being, attracting top talent globally.
- Salesforce: Their 1-1-1 philanthropic model and 'Ohana' culture emphasize giving back and creating a strong sense of community.
- Microsoft: The transformation under Satya Nadella fostered a growth mindset culture, revitalizing the company's image and attracting a new generation of talent.
- Airbnb: Their 'Belong Anywhere' philosophy extends to the employee experience, fostering a sense of inclusion and global connection.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Audit: Conduct a thorough audit of your current employee experience before developing your strategy.
- Involve Employees: Include employees from all levels in the EVP development process to ensure authenticity and buy-in.
- Targeted Messaging: Create specific messaging tailored to different talent segments.
- Train Hiring Managers: Equip hiring managers to consistently communicate the employer brand throughout the recruitment process.
- Employee Stories: Leverage employee stories as authentic and engaging content for your employer branding efforts.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Reduced recruitment costs by attracting better-qualified candidates.
- Decreased turnover by improving employee engagement and satisfaction.
- Enhanced competitive advantage in talent acquisition.
- Creation of authentic brand ambassadors from within.
- Reinforced overall corporate brand perception.
Cons:
- Requires significant internal alignment and cultural work.
- Can backfire if external promises don't match the internal reality.
- Difficult to measure direct ROI.
- Needs constant maintenance and evolution.
- May expose internal weaknesses during the development process.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Employer branding is essential for any organization looking to attract and retain top talent, particularly in competitive industries. It becomes even more crucial during periods of growth, expansion, or when seeking to reposition the company's image. Learn more about Employer Branding Strategy
This approach deserves its place in the list of corporate branding strategies because it recognizes the intrinsic link between a strong internal culture and a powerful external brand. By investing in your employees, you're not just building a better workplace; you're building a stronger brand, a more resilient organization, and a more attractive proposition for investors, partners, and customers. The contributions of thought leaders like LinkedIn, Richard Mosley (author of 'Employer Brand Management'), Glassdoor, and SHRM have significantly popularized and advanced the field of employer branding, solidifying its importance in the broader corporate branding landscape.
5. Digital-First Branding Strategy
In today's interconnected world, a robust online presence is no longer optional—it's essential. For Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, corporate marketing teams, venture capital firms, and even event coordinators, a digital-first branding strategy is paramount among corporate branding strategies. This approach prioritizes digital channels, platforms, and experiences as the primary means of building and expressing a corporate brand. Rather than simply adapting traditional branding efforts for a digital audience, a digital-first strategy designs brand elements, interactions, and communications specifically for digital-native audiences and environments from the outset. This allows brands to connect with their target audience where they spend the majority of their time, fostering deeper engagement and building stronger relationships.
A digital-first branding strategy is characterized by several key features:
- Mobile-optimized brand experiences: Recognizing that a significant portion of online interaction happens on mobile devices, everything from websites to email campaigns must be seamlessly accessible and engaging on smaller screens.
- Social media-centric content strategy: Content is tailored for various social media platforms, encouraging sharing and community building. This includes utilizing platform-specific features like Instagram Stories, TikTok trends, or LinkedIn articles.
- Interactive brand elements: Logos, graphics, and other visual assets are designed with digital interactivity in mind, incorporating animation, micro-interactions, and dynamic elements to capture attention and enhance engagement.
- Data-driven personalization capabilities: Leveraging data analytics to understand customer preferences and behaviors, brands can personalize content, offers, and experiences to create more relevant and impactful interactions.
- Omnichannel consistency with digital at the core: While a digital-first strategy prioritizes online channels, it also ensures brand consistency across all touchpoints, including offline interactions, with the digital experience serving as the central hub.
- Real-time brand engagement capabilities: The ability to respond quickly and effectively to trending topics, customer feedback, and real-time events is crucial for building brand relevance and fostering a sense of community.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Glossier: Built a highly successful beauty brand primarily through Instagram, leveraging user-generated content and community engagement.
- Spotify: Offers data-driven personalized experiences, culminating in their popular annual Wrapped campaign, which showcases individual listening habits.
- Burberry: Successfully transformed from a traditional luxury brand to a digital innovator, embracing new technologies and online platforms to connect with a younger audience.
- Oreo: Demonstrated the power of real-time marketing during the 2013 Super Bowl blackout with their quick-witted tweet, setting a new standard for reactive brand engagement.
Pros of a Digital-First Approach:
- Relevance: Connects with digital-native consumers in their preferred environments.
- Personalization: Enables targeted messaging and tailored experiences.
- Agility: Facilitates rapid iteration and optimization based on data insights.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often more affordable than traditional media campaigns.
- Measurable Results: Provides richer analytics and measurement capabilities.
Cons to Consider:
- Exclusion: Can alienate non-digital audience segments.
- Platform Dependence: Requires constant adaptation to platform changes and algorithm updates.
- Digital Fatigue: Risks contributing to consumer overload in a saturated digital landscape.
- Brand Safety: Increased exposure to potential brand safety and context issues.
- Channel Consistency: Maintaining brand consistency across a growing number of digital channels can be challenging.
Actionable Tips for Implementing a Digital-First Strategy:
- Design for Digital: Create brand assets specifically optimized for digital platforms and user experiences.
- Modular Brand Systems: Develop adaptable brand systems that can be easily deployed across various channels and devices.
- Data as an Asset: Prioritize building first-party data capabilities to understand your audience and personalize their experience.
- Establish a Clear Voice: Define a consistent brand voice and tone for all digital communications.
- Long-Term Vision: Balance real-time engagement with a long-term strategic approach to brand building.
Learn more about Digital-First Branding Strategy
Digital-first branding, popularized by direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands, figures like Emily Weiss (Glossier founder) and Gary Vaynerchuk (digital marketing expert), and companies like Salesforce, offers a powerful framework for building a relevant and resonant brand in the digital age. It deserves a place in any discussion about corporate branding strategies because it acknowledges the fundamental shift in how consumers interact with brands, placing digital at the heart of the brand experience. By embracing a digital-first approach, organizations can connect with their target audience on a deeper level, build stronger relationships, and achieve greater success in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
6. Co-Branding Strategy
Co-branding, a powerful corporate branding strategy, involves a strategic partnership between two or more brands to create a new product, service, or marketing initiative. This collaborative approach leverages the combined brand equities, audiences, and strengths of the participating companies to achieve mutually beneficial outcomes. By transferring positive associations between brands, co-branding aims to reach new audiences and create offerings with enhanced perceived value, making it a valuable tool in any organization's arsenal of corporate branding strategies.
How Co-Branding Works:
Co-branding initiatives are built on a foundation of shared objectives and complementary brand identities. The process typically involves:
- Strategic Alignment: Identifying partner brands whose values, target audiences, and market positioning align with your own.
- Shared Equity and Access: Leveraging each other's brand equity and existing customer base to expand reach and credibility.
- Combined Resources: Pooling marketing resources and capabilities to maximize the impact of the collaboration.
- Joint Development/Promotion: Working together to develop new products, services, or co-branded marketing campaigns.
- Formal Agreements: Establishing clear legal agreements regarding brand usage, representation, and profit sharing.
Illustrative Examples:
Several successful co-branding partnerships demonstrate the potential of this strategy:
- Nike + Apple (Nike+): This collaboration combined Nike's expertise in athletic wear with Apple's technological prowess to create a seamless fitness tracking experience.
- Spotify + Starbucks: This partnership integrated Spotify's music streaming platform into the Starbucks rewards program, offering exclusive content and driving customer engagement for both brands.
- GoPro + Red Bull: These two brands, both deeply rooted in extreme sports and adventure, have collaborated on numerous content creation projects, amplifying their shared brand message.
- BMW + Louis Vuitton: This luxury partnership resulted in a bespoke luggage collection designed specifically for BMW vehicles, appealing to a shared affluent customer base.
Actionable Tips for Effective Co-Branding:
- Choose Wisely: Partner with brands whose values complement, not compete with, your own. A strong strategic fit is crucial for success.
- Establish Clear Governance: Define a clear governance structure outlining roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes before launching the partnership.
- Brand Usage Guidelines: Create detailed brand usage guidelines to ensure consistent brand representation across all co-branded materials.
- Define Success Metrics: Establish measurable success metrics that align with both partners' objectives.
- Plan an Exit Strategy: While hoping for the best, always plan for potential challenges and define an exit strategy in advance.
- Test Consumer Perception: Conduct thorough market research to gauge consumer perception of the partnership and identify potential risks or opportunities.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Expanded reach to a partner's audience with built-in credibility
- Creation of differentiated offerings in competitive markets
- Shared development and marketing costs
- Generation of news value and increased media attention
- Combination of complementary brand strengths
Cons:
- Potential brand dilution if the partnership isn't aligned
- Complex governance and decision-making processes
- Risk exposure if a partner faces reputational issues
- Challenges in maintaining consistent brand experiences
- Potential confusion about brand ownership
Why Co-Branding Deserves Its Place:
Co-branding earns its spot as a key corporate branding strategy due to its potential to amplify brand reach, create unique value propositions, and generate significant marketing synergy. When executed effectively, it offers a powerful way to leverage existing brand equity and access new markets, making it a valuable tool for Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, and corporate marketing teams alike. It also offers exciting opportunities for venture capital firms seeking innovative brand collaborations and event coordinators looking to create memorable brand experiences. The examples of successful co-branding partnerships, such as the ongoing collaborations between Star Wars and LEGO, H&M's designer collaborations, Mastercard's extensive partnership network, and Betty Crocker and Hershey's, further underscore the effectiveness and versatility of this strategy within the broader landscape of corporate branding strategies.
7. Storytelling Brand Strategy
Storytelling brand strategy stands out among corporate branding strategies as a powerful way to connect with audiences on an emotional level. Instead of relying on traditional, feature-driven marketing, this approach leverages narrative techniques to communicate a brand's values, history, purpose, and differentiators through compelling stories. This resonates with human experiences, making brand messages more memorable and impactful than simple product claims. By placing the brand within a meaningful narrative, storytelling fosters deeper engagement and strengthens brand loyalty. This is crucial for Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, corporate marketing teams, venture capital firms, and even event coordinators seeking to create lasting impressions.
This method involves crafting a narrative framework for brand communications, complete with character development (often casting the brand as a hero or guide), an emotional arc that resonates with audience values, and consistent story elements across all touchpoints. This provides a robust structure for consistent messaging and offers multi-channel storytelling opportunities, often incorporating user/customer stories as core content.
Think of Nike's athlete-centered stories of overcoming obstacles. They don't just sell shoes; they sell inspiration and the pursuit of greatness. Airbnb's "Belong Anywhere" narrative and host/guest stories connect travelers with unique experiences and local communities, going beyond simply offering accommodation. Dove's Real Beauty campaign challenged beauty standards, fostering a conversation about self-acceptance and body positivity. These examples illustrate the power of storytelling to transcend product features and resonate with deeper human values. Similarly, Google's 'Search On' stories highlight the positive human impact of their technology, while John Deere's long-standing content platform 'The Furrow' has firmly established their agricultural expertise by sharing compelling stories related to farming and the people behind it.
Features of Storytelling Brand Strategy:
- Narrative framework for brand communications: Providing a consistent structure for all messaging.
- Character development: Defining roles and personalities, including the brand's role in the narrative.
- Emotional arc: Crafting stories that resonate with audience values and evoke desired emotions.
- Consistent story elements across touchpoints: Ensuring a unified brand experience across all channels.
- Multi-channel storytelling opportunities: Leveraging diverse platforms to reach target audiences.
- User/customer stories as core content: Amplifying authentic experiences and building trust.
Pros:
- Creates stronger emotional connections: Compared to feature-based messaging, storytelling forges deeper bonds with audiences.
- Makes complex brand values more accessible and memorable: Simplifying communication and increasing retention.
- Differentiates brand in commoditized markets: Standing out through unique narratives and brand personality.
- Provides framework for consistent communication: Ensuring clarity and cohesion across all marketing efforts.
- Engages audiences more effectively than traditional advertising: Capturing attention and fostering deeper engagement.
Cons:
- Can become self-indulgent if not audience-focused: Losing sight of the target audience and their needs.
- Requires significant content creation resources: Demanding investment in skilled writers, videographers, and other creatives.
- May not communicate product benefits effectively: Potentially overshadowing key features and functionalities.
- Challenging to measure direct business impact: Difficulty quantifying the ROI of storytelling initiatives.
- Risk of appearing inauthentic if stories don't align with reality: Damaging brand credibility if narratives are perceived as fabricated or misleading.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Storytelling:
- Identify core narratives that reflect authentic brand truths: Base stories on genuine values and experiences.
- Develop brand story framework with key plot points: Create a structured narrative arc for consistency.
- Create story collection processes within organization: Gather authentic stories from employees and customers.
- Train teams on storytelling techniques: Equip staff with the skills to effectively craft and communicate narratives.
- Map stories to different stages of customer journey: Tailor narratives to resonate with specific customer needs and touchpoints.
- Test emotional impact of stories with target audiences: Gather feedback and refine narratives for optimal resonance.
Pioneering figures like Joseph Campbell (Hero's Journey framework), Donald Miller (StoryBrand methodology), Pixar (corporate storytelling techniques), and Seth Godin (marketing storytelling) have significantly popularized the power of narrative in branding. Learn more about Storytelling Brand Strategy
When aiming to build lasting brand loyalty, create meaningful differentiation, and foster emotional connections, storytelling provides an invaluable framework for corporate branding strategies. This approach is particularly well-suited for businesses operating in competitive markets where traditional, feature-based marketing falls flat. By tapping into universal human experiences and values, storytelling resonates on a deeper level, transforming brand messaging from mere advertising into a powerful form of connection and engagement.
8. Experiential Branding Strategy
Experiential branding is a powerful corporate branding strategy that moves beyond traditional advertising and focuses on crafting immersive, multi-sensory experiences. It's about creating engaging interactions that allow consumers to directly experience a brand's values, personality, and products or services in a tangible way. Rather than simply telling customers about your brand, you're showing them, allowing them to participate and form their own emotional connections. This strategy leverages physical spaces, events, activations, and even digital platforms to create holistic brand experiences that resonate deeply with the target audience. This approach is particularly effective in today’s competitive landscape, where consumers are increasingly seeking authentic and meaningful interactions with the brands they choose.

Experiential branding involves creating multi-sensory touchpoints – engaging sight, sound, touch, taste, and even smell – to deepen the impact. It incorporates interactive elements and participatory opportunities that encourage active involvement from the customer. Whether it’s a physical pop-up shop or a digital interactive game, the goal is to immerse the consumer in the brand world. This strategy recognizes that consistent experience design across all interactions, both physical and digital, is key to building a cohesive and impactful brand image.
Successful examples of experiential branding abound. Apple stores have revolutionized retail by creating interactive experience centers where customers can explore and engage with products. Starbucks' "third place" concept fosters community and connection beyond just selling coffee. Red Bull's association with extreme sports events builds a strong brand identity around adventure and adrenaline. Sephora's in-store beauty testing environments offer personalized experiences, while Mastercard's "Priceless" experiences platform provides exclusive access to curated events and activities, connecting with consumers on an emotional level.
Why use experiential branding? It deserves its place in any comprehensive list of corporate branding strategies because it offers distinct advantages. It creates deeper emotional connections with customers, leading to more memorable brand impressions. It allows for brand differentiation that is difficult for competitors to replicate. It generates authentic user-generated content and positive word-of-mouth marketing. Experiential branding also provides valuable first-party behavioral data that can inform future marketing efforts. Ultimately, it transforms customers into brand advocates through memorable and shareable experiences.
Pros:
- Creates deeper emotional connections and memorable impressions.
- Differentiates brand in ways competitors cannot easily copy.
- Generates authentic user-generated content and word-of-mouth.
- Provides valuable first-party behavioral data.
- Turns customers into brand advocates through memorable experiences.
Cons:
- Typically higher investment than traditional branding.
- Challenging to scale consistently across markets.
- Requires cross-functional expertise (design, technology, operations).
- Difficult to measure ROI with traditional metrics.
- High customer expectations once an experiential standard is set.
Tips for implementing experiential branding:
- Map the entire customer journey: Identify opportunities for experiential touchpoints at every stage.
- Identify signature moments: Define the key interactions that will define the brand experience.
- Design for consistency: Ensure a seamless and integrated experience across both physical and digital channels.
- Train your staff: Frontline employees are crucial for delivering a positive brand experience.
- Capture experience data: Collect feedback and data to continuously improve and refine the experience.
- Create shareable moments: Encourage social sharing and user-generated content.
Experiential branding, popularized by thought leaders like Pine & Gilmore (authors of "The Experience Economy") and pioneered by companies like Disney, Glossier, and Nike, is an essential strategy for companies seeking to build strong, lasting relationships with their customers in today's experience-driven economy. For Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, corporate marketing teams, venture capital firms, and event coordinators alike, understanding and implementing experiential branding can be a game-changer.
Corporate Branding Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Architecture Strategy | High – complex across large orgs | High – significant consistency effort | Clear brand hierarchy and efficient portfolio management | Multi-brand companies managing diverse portfolios | Clarity on brand relationships; leverages brand equity |
| Brand Positioning Strategy | Medium – requires deep market research | Medium – investment in competitive analysis | Strong market differentiation and consistent messaging | Brands needing clear market positioning | Distinctive value proposition; supports premium pricing |
| Purpose-Driven Branding Strategy | Medium-High – aligning mission & ops | High – operational changes and storytelling | Deeper emotional connections; positive social impact | Companies seeking social/environmental impact | Builds loyalty; attracts purpose-driven consumers |
| Employer Branding Strategy | Medium-High – internal culture alignment | Medium-High – ongoing employee engagement | Reduced recruitment costs; stronger talent acquisition | Organizations focused on talent attraction/retention | Enhances employee engagement; authentic brand ambassadors |
| Digital-First Branding Strategy | Medium – adapts to fast digital shifts | Medium – digital tools and content creation | Rapid iteration; personalized digital experiences | Brands targeting digital-native audiences | Cost-effective; data-driven personalization |
| Co-Branding Strategy | High – complex partner governance | Medium-High – shared development & marketing | Expanded reach; combined brand strengths | Strategic partnerships aiming for new audiences | Access new markets; cost sharing; enhanced credibility |
| Storytelling Brand Strategy | Medium – requires ongoing content creation | Medium – creative resources | Strong emotional resonance and memorable brand narratives | Brands wanting deep audience engagement | Differentiates in crowded markets; consistent messaging |
| Experiential Branding Strategy | High – cross-functional design effort | High – investment in immersive experiences | Memorable brand interactions; strong emotional engagement | Brands prioritizing immersive consumer experiences | Differentiates uniquely; drives advocacy and word-of-mouth |
Creating a Powerful Brand Legacy
Mastering corporate branding strategies is essential for long-term success. From defining your brand architecture and positioning to embracing purpose-driven initiatives and digital-first approaches, each strategy discussed in this article plays a crucial role in shaping a compelling brand identity. Effectively leveraging these strategies—including co-branding, storytelling, and experiential marketing—enables companies to differentiate themselves, build customer loyalty, and ultimately achieve sustainable growth. Remember, consistency and authenticity are the cornerstones of a resonant brand that stands the test of time.
These corporate branding strategies are particularly relevant for Fortune 100 companies, tech startups, corporate marketing teams, venture capital firms, and even event coordinators looking to create impactful experiences. By understanding and implementing these core concepts, you're not just building a brand, you're crafting a legacy. A strong brand legacy is built on trust and positive perception. This requires ongoing management of your brand's online presence and reputation. For expert guidance on this crucial aspect, explore resources on brand reputation management from Notifyio.
Building a memorable brand also involves reinforcing your identity through tangible touchpoints. Elevate your corporate branding strategies with high-quality, custom branded merchandise. Explore the range of customizable electronic products offered by Electronic Finishing Solutions and discover how they can help bring your brand vision to life and leave a lasting impression.



