Unlocking Hidden Value: Beyond Price in Corporate Spending
In a competitive business environment, both established corporations and agile startups face constant pressure to optimize spending and enhance profitability. Effective procurement has evolved far beyond simply haggling for the lowest price; it is now a critical strategic function capable of unlocking immense value and driving sustainable growth. The primary challenge lies in moving from traditional, transactional purchasing to implementing sophisticated, data-driven procurement cost savings strategies. This shift requires a new mindset, a commitment to technology, and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
This comprehensive guide moves past generic advice to deliver actionable insights on transforming your procurement operations. We will explore seven powerful and proven strategies that procurement teams can implement to achieve significant, measurable cost reductions and improve overall efficiency. These methods provide a clear roadmap for turning your procurement function into a true competitive advantage.
From leveraging advanced analytics for strategic sourcing to harnessing the power of automation and conducting thorough Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis, this article is designed for immediate application. We will detail practical implementation steps, explore real-world scenarios, and provide specific examples to help you navigate the complexities of modern procurement. Prepare to discover how to not only cut costs but also build stronger supplier relationships, mitigate risks, and deliver tangible results directly to your bottom line.
1. Strategic Sourcing
Strategic sourcing elevates procurement from a transactional function to a core business discipline. Instead of merely processing purchase orders, it’s a proactive and analytical methodology for continuously re-evaluating and improving an organization’s purchasing activities. This approach systematically analyzes spend data, scrutinizes market dynamics, and develops comprehensive sourcing strategies that are directly aligned with overarching business objectives. It fundamentally shifts the focus from the initial purchase price to the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes all costs associated with a product or service, such as maintenance, operational expenses, and end-of-life disposal.

The power of strategic sourcing is well-documented. For instance, General Electric famously leveraged this approach across more than 300 spending categories to generate over $8 billion in annual savings. Similarly, IBM's adoption of category-based strategic sourcing led to a 15% reduction in procurement costs while simultaneously enhancing supplier performance and reliability. These examples highlight how a structured sourcing process can deliver significant, measurable financial benefits.
How to Implement Strategic Sourcing
To effectively deploy strategic sourcing, procurement teams should follow a structured, multi-step process.
-
Analyze Spend: The first step is to gain complete visibility into corporate spending. Invest in procurement analytics tools to consolidate and categorize all spend data. Identify who is buying what, from which suppliers, and at what price. This analysis will reveal high-spend, high-opportunity categories. For essential services like connectivity, strategic sourcing involves evaluating and selecting the best business phone and internet providers that align with your long-term goals and deliver optimal value.
-
Assess the Market: For each priority category, conduct a thorough market analysis. Understand the supply base, market trends, pricing models, and competitive landscape. Identify key cost drivers and potential risks, such as supply chain disruptions or regulatory changes.
-
Develop a Strategy: Create a specific sourcing strategy for each category. This isn't a one-size-fits-all approach. Your strategy might involve consolidating suppliers, seeking out new partners, engaging in competitive bidding, or forming long-term strategic alliances. The strategy must align with business needs, whether that’s cost reduction, innovation, or risk mitigation.
-
Execute and Manage: Implement your strategy through structured negotiation and contracting. Establish clear governance with cross-functional teams involving stakeholders from finance, operations, and the relevant business units. Develop robust supplier scorecards with metrics for quality, delivery, innovation, and cost to continuously monitor and manage performance. This structured approach is one of the most reliable procurement cost savings strategies for long-term value creation.
2. Supplier Consolidation
Supplier consolidation is a powerful procurement strategy focused on intentionally reducing the total number of suppliers an organization works with. Instead of spreading purchases across a wide array of vendors, this approach concentrates spending with a smaller group of high-performing, strategic partners. By increasing the volume of business with these select suppliers, companies can leverage significant economies of scale to negotiate more favorable pricing, better payment terms, and enhanced service level agreements. This simplification not only drives down direct costs but also streamlines administrative processes, reducing the complexity and overhead associated with managing a large supplier base.

The impact of a well-executed consolidation effort can be profound. For example, Ford Motor Company drastically cut its supplier base from over 3,000 to around 1,000, which contributed to a 20% reduction in costs and fostered deeper innovation with its key partners. Similarly, Johnson & Johnson streamlined its vendor list from a staggering 40,000 down to 9,000, realizing an estimated $2.5 billion in savings over five years. These cases demonstrate that consolidating suppliers is one of the most effective procurement cost savings strategies for achieving both financial efficiency and stronger supply chain relationships.
How to Implement Supplier Consolidation
A successful supplier consolidation initiative requires careful planning and a phased approach to minimize risk and maximize returns.
-
Analyze the Supplier Base: Begin with a comprehensive analysis of your current suppliers, similar to a spend analysis. Segment suppliers by category, spend volume, and performance. Identify redundant suppliers providing similar goods or services and pinpoint categories where consolidation offers the greatest potential for savings.
-
Assess Supplier Performance and Risk: Don't consolidate based on cost alone. Evaluate suppliers using a robust scorecard that includes metrics for quality, on-time delivery, financial stability, and innovation capacity. A thorough risk assessment is crucial; you must understand the potential impact of relying more heavily on fewer suppliers.
-
Develop the Consolidation Plan: Create a clear strategy outlining which suppliers will be retained, consolidated, or phased out. Define the transition timeline and communication plan for all affected internal stakeholders and suppliers. For critical categories, ensure you maintain qualified backup suppliers to mitigate supply chain risks.
-
Negotiate and Strengthen Partnerships: Approach your chosen strategic suppliers to negotiate new, long-term agreements. Use your increased purchasing power as leverage for better pricing, volume discounts, and performance-based incentives. The goal is to move from a transactional relationship to a true strategic partnership that drives mutual value and continuous improvement.
3. E-Procurement and Automation
E-procurement and automation represent the digital transformation of the procurement lifecycle, moving organizations from manual, paper-based workflows to streamlined, automated systems. This strategy leverages digital platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotic process automation (RPA) to manage everything from requisition and purchase orders to invoicing and payment. By digitizing these core functions, businesses can significantly reduce manual effort, minimize human error, improve policy compliance, and unlock substantial cost savings through enhanced process efficiency and real-time spend visibility.
The impact of this digital shift is profound. For example, Siemens deployed SAP Ariba across its global operations in 190 countries, which resulted in a 12% reduction in procurement costs and slashed procurement cycle times by 50%. Similarly, Unilever’s e-procurement platform now handles over $13 billion in annual spend, achieving a 25% saving in processing costs. Microsoft has also seen remarkable gains, using an AI-powered system that cut its contract review time from weeks down to a matter of hours, showcasing how automation accelerates critical business processes.
The infographic below highlights the typical performance gains organizations can expect from implementing e-procurement solutions.
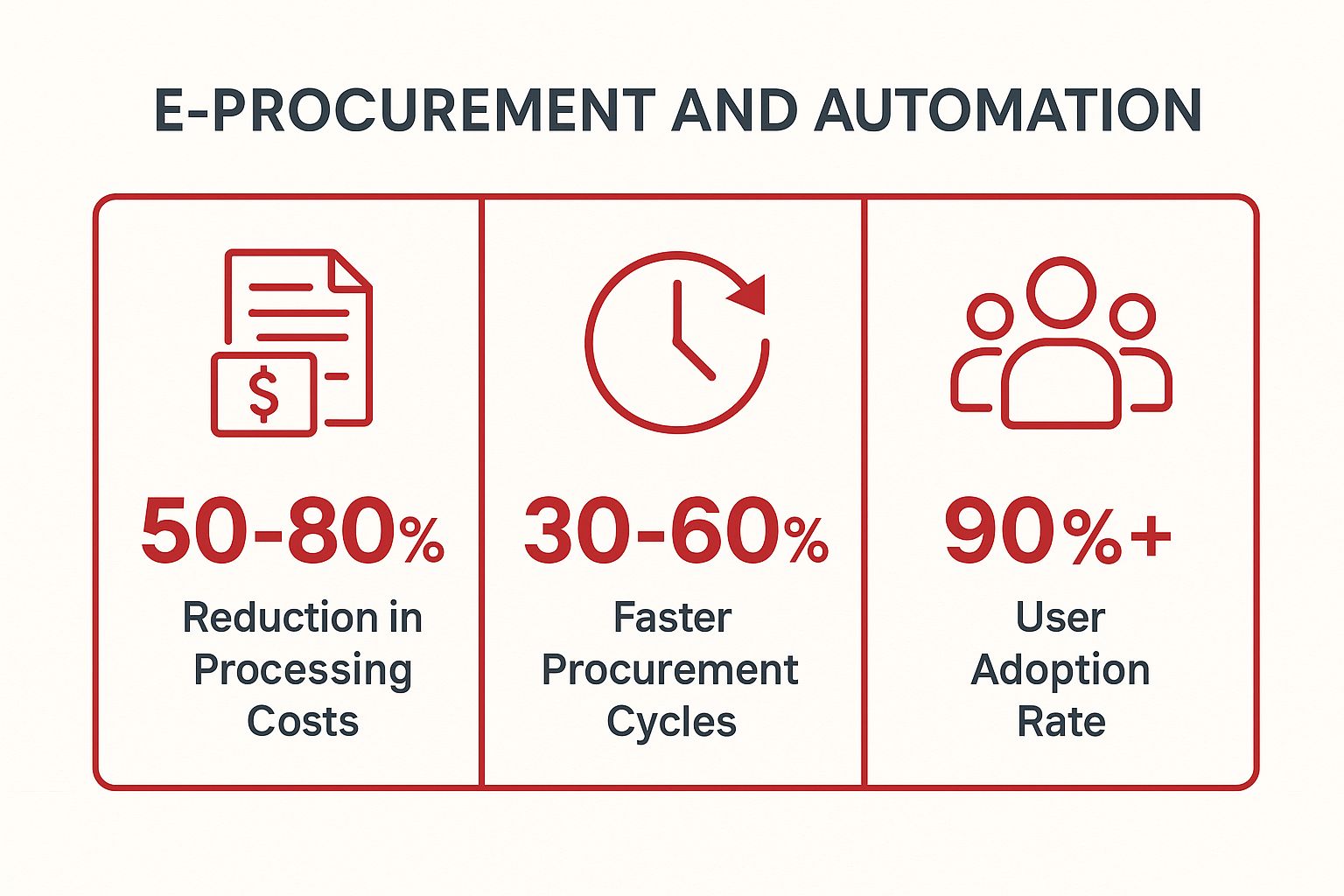
These figures demonstrate that the benefits extend beyond simple cost-cutting to create faster, more efficient, and user-friendly procurement ecosystems.
How to Implement E-Procurement and Automation
Successfully integrating automation requires a strategic and phased approach to maximize adoption and ROI.
-
Start with a Pilot Program: Avoid a "big bang" implementation. Instead, launch a pilot program in a specific, low-risk category or a single business unit. This allows you to test the technology, gather user feedback, and build a strong business case with measurable results before a full-scale rollout.
-
Ensure Executive Sponsorship: Digital transformation is a significant change. Secure strong, visible sponsorship from executive leadership to champion the initiative, allocate necessary resources, and drive the change management process. Their support is crucial for overcoming resistance and aligning the project with broader business goals.
-
Integrate with Existing Systems: For seamless data flow and a single source of truth, ensure the new e-procurement platform integrates smoothly with your existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and financial systems. This integration prevents data silos and automates the entire procure-to-pay cycle. As businesses increasingly leverage these digital tools, understanding effective strategies for cloud cost optimization also becomes crucial for maintaining financial efficiency.
-
Prioritize User Training and Support: Technology is only effective if people use it. Develop a comprehensive training program tailored to different user roles and provide ongoing support through help desks, tutorials, and user guides. A positive user experience is key to achieving high adoption rates and realizing the full potential of your investment in these procurement cost savings strategies.
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis is a financial framework that moves procurement decisions beyond the initial purchase price to evaluate the complete cost of an asset or service over its entire lifecycle. This comprehensive approach factors in all direct and indirect expenses, including acquisition, implementation, operation, maintenance, training, and end-of-life disposal. By quantifying these often-hidden costs, TCO enables organizations to make more intelligent, value-driven purchasing decisions that optimize long-term financial performance. It fundamentally reframes the procurement question from "What is the cheapest option now?" to "What is the most cost-effective solution over time?"

The transformative impact of TCO is evident across various industries. The U.S. Navy, a long-time proponent of lifecycle cost analysis, has used TCO to reduce shipbuilding costs by up to 30% by optimizing designs for long-term maintenance and operational efficiency. Similarly, Xerox successfully used TCO models to demonstrate how its enterprise printing solutions delivered up to 40% lower costs than competitors when accounting for consumables, service, and energy use. These examples underscore how a TCO-centric view reveals the true value of a purchase, making it one of the most powerful procurement cost savings strategies.
How to Implement TCO Analysis
Adopting a TCO model requires a disciplined and collaborative approach to cost identification and calculation.
-
Develop Standardized Models: Create standardized TCO templates for recurring procurement categories like IT hardware, software, or fleet vehicles. This ensures consistency and comparability. Break the model into key cost buckets: acquisition (price, shipping, installation), operating (energy, consumables, labor), maintenance (repairs, service contracts), and disposal (decommissioning, resale value).
-
Involve All Stakeholders: Conduct cross-functional workshops involving teams from IT, finance, operations, and the end-user department. These stakeholders possess critical insights into hidden costs, such as user training requirements, operational downtime risks, or specific maintenance needs that a procurement professional might overlook.
-
Validate with Data and Scenarios: Use historical performance data and industry benchmarks to validate your cost assumptions and build realistic models. Don't stop at a single forecast. Run sensitivity analysis and consider different risk scenarios, such as fluctuating energy prices or unexpected maintenance events, to understand the potential range of outcomes.
-
Update and Refine: TCO is not a one-time calculation. Regularly update your models with actual performance data once an asset is in use. This feedback loop allows you to refine your future TCO calculations, making them increasingly accurate and reliable for subsequent procurement decisions. This iterative process ensures your TCO framework evolves and continues to deliver value.
5. Reverse Auctions
Reverse auctions flip the traditional procurement model on its head, creating a dynamic, real-time competitive bidding environment. Instead of sellers setting a price and buyers choosing, buyers specify their requirements, and pre-qualified suppliers bid against each other to win the business. Prices progressively decrease as suppliers compete, directly driving down acquisition costs. This method leverages market competition to its fullest extent, ensuring the buyer achieves the best possible market price at that specific moment, all while maintaining a transparent and fair selection process.
This strategy's effectiveness is proven by major corporations. General Motors famously utilized reverse auctions for indirect materials and services, realizing savings of $2.6 billion. Similarly, British Telecom adopted this approach for IT hardware procurement and saw its costs drop by 15%. Procter & Gamble also achieved an impressive 12% average savings on manufacturing equipment by embracing online reverse auctions. These cases demonstrate that when applied correctly, reverse auctions are a powerful tool for immediate cost reduction.
How to Implement Reverse Auctions
Deploying reverse auctions requires careful planning and execution to maximize benefits without sacrificing quality or damaging supplier relationships.
-
Select Appropriate Categories: This method is not suitable for all purchases. It works best for goods and services that are standardized, have clear and well-defined specifications, and where the primary decision driver is price. Think commodity items like office supplies, standard IT hardware, or certain MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) components. Avoid using it for highly complex, strategic, or relationship-driven services.
-
Qualify and Prepare Suppliers: The success of an auction depends on robust competition. Ensure you have a pool of at least 3-5 pre-qualified suppliers ready to participate. Pre-qualification is key; screen suppliers based on quality, capacity, and financial stability before the auction begins. Provide all bidders with comprehensive training on the auction software and clear guidelines on the event rules to ensure a level playing field.
-
Define Clear Event Rules: Establish unambiguous terms before the auction starts. This includes defining the exact technical specifications of the product or service, outlining logistics and delivery requirements, and clarifying the evaluation criteria. While price is the focus, it shouldn't be the only factor. Decide how non-price attributes like delivery lead times or warranty terms will be weighted, if at all.
-
Manage the Auction and Post-Auction Process: Monitor the auction in real-time to ensure it runs smoothly and address any technical issues. After the auction concludes, remember that the lowest bidder isn't automatically the winner unless you've established a "price-only" event. Evaluate the final bids against your pre-defined criteria and award the business accordingly. Critically, always balance the immediate savings from this tactic with the long-term need for quality and reliable supplier partnerships, making it one of the most impactful procurement cost savings strategies for specific spend categories.
6. Make vs. Buy Analysis
Make vs. buy analysis is a fundamental strategic decision-making process used to determine whether an organization should produce goods or services internally or purchase them from an external supplier. This evaluation moves beyond a simple price comparison to a comprehensive assessment of quantitative and qualitative factors. It involves a deep dive into costs, core competencies, production capacity, quality control, and strategic risks. By systematically weighing these elements, companies can identify the most financially sound and strategically advantageous sourcing path for any given product or service, ensuring resources are allocated effectively.
The strategic power of make vs. buy decisions is evident across industries. For example, Nike famously decided to outsource nearly all its manufacturing to focus on its core competencies: design, branding, and marketing. This move is credited with helping reduce production costs by an estimated 30% and enabling global scale. Conversely, after years of outsourcing, Ford Motor Company began insourcing key software development for its infotainment and connectivity systems. This strategic shift helped reduce development costs by over 20% while accelerating innovation and improving the end-user experience. These examples show how a well-executed make vs. buy analysis can unlock significant value.
How to Implement Make vs. Buy Analysis
To conduct a robust make vs. buy analysis, procurement and operations teams should adopt a structured, data-driven methodology.
-
Conduct Thorough Cost Analysis: The initial step is to compare the full costs of both options. For the "make" option, conduct a detailed activity-based costing exercise to capture all direct and indirect costs, including labor, materials, overhead, and equipment depreciation. For the "buy" option, evaluate supplier pricing models, including all associated costs like shipping, tariffs, and supplier management. This comparison provides the quantitative foundation for the decision.
-
Assess Capabilities and Strategic Importance: Evaluate whether the product or service is a core competency or a commodity. If it is central to your competitive advantage or involves proprietary intellectual property, making it in-house may be preferable to protect it. If it is a non-core, standardized item, outsourcing to a specialized supplier is often more efficient.
-
Evaluate Risks and Quality: Analyze the potential risks associated with each path. Outsourcing can introduce risks related to supply chain disruptions, quality control issues, or data security. In-house production carries risks such as high capital investment, operational inefficiencies, and demand volatility. Assess the impact each option would have on quality, delivery consistency, and overall customer satisfaction.
-
Develop a Transition and Management Plan: Regardless of the final decision, create a detailed implementation plan. If you decide to "make," this includes plans for capacity building and resource allocation. If you decide to "buy," it involves a rigorous supplier selection, negotiation, and onboarding process. This structured analysis is one of the most impactful procurement cost savings strategies for aligning operational execution with long-term business goals.
7. Global Sourcing and Low-Cost Country Sourcing
Global sourcing is a strategic approach that involves identifying, evaluating, and sourcing goods and services from suppliers located anywhere in the world. A key subset of this strategy, Low-Cost Country Sourcing (LCCS), specifically targets suppliers in developing economies to leverage cost advantages driven by lower labor rates, raw material access, and favorable economic conditions. This moves beyond domestic procurement to tap into a global marketplace, unlocking significant cost reductions and accessing new technologies and production capabilities that may not be available locally.
The financial impact of a well-executed global sourcing strategy can be transformative. Apple's extensive supply chain in Asia, for example, is a cornerstone of its business model, reportedly providing cost advantages of 30-40% in electronics manufacturing. Similarly, retail giant IKEA maintains a vast global sourcing network across more than 50 countries, enabling it to achieve costs up to 25% lower than if it relied solely on domestic alternatives. These cases demonstrate how leveraging global cost arbitrage can create a powerful competitive advantage.
How to Implement Global Sourcing
Successfully navigating international procurement requires a structured and risk-aware methodology to capture the benefits while mitigating potential challenges.
-
Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Before engaging any international supplier, perform rigorous audits and capability assessments. This goes beyond a simple price check to include evaluations of their manufacturing processes, financial stability, ethical labor practices, and technological infrastructure. The initial investment in due diligence prevents costly quality failures and supply disruptions later.
-
Establish a Local Presence: Navigating cultural nuances, regulations, and logistics in a foreign market can be challenging. Consider establishing a small, local sourcing office or partnering with reputable on-the-ground sourcing agents or consultants. These local experts can facilitate communication, manage supplier relationships, and conduct quality inspections more effectively.
-
Calculate Total Landed Cost: The sticker price from a low-cost country supplier is only part of the equation. A critical step is to calculate the Total Landed Cost, which includes the purchase price plus all logistics, shipping fees, insurance, customs duties, taxes, and currency conversion fees. This comprehensive calculation provides a true picture of the potential savings and is essential for making an informed sourcing decision.
-
Implement Robust Contracts and Quality Control: Create detailed, legally binding contracts that clearly define quality standards, delivery schedules, payment terms, and crucial intellectual property (IP) protections. Do not rely on handshakes or informal agreements. Implement a multi-stage quality control process, including pre-production sample approval, in-process inspections, and final pre-shipment inspections to ensure standards are met before goods leave the factory. This proactive approach makes global sourcing one of the most potent procurement cost savings strategies available.
Procurement Cost Savings Strategies Comparison
| Procurement Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Sourcing | High: complex analytics, cross-functional teams | High: data analytics, time, cross-team effort | Significant cost savings (5-20%), risk reduction | High-spend categories, multiple categories | Data-driven decisions, long-term supplier partnerships |
| Supplier Consolidation | Medium: supplier evaluation, contract standardization | Medium: supplier monitoring, negotiations | Cost savings (10-25%), reduced admin burden | Simplifying supplier base, volume aggregation | Lower transaction costs, enhanced negotiation power |
| E-Procurement and Automation | High: technology implementation, integration | High: software, training, change mgmt | Major process speedup (30-60%), cost reduction | Process automation, compliance improvement | Real-time analytics, reduced manual effort |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis | High: extensive data collection and modeling | High: data, lifecycle analysis expertise | Better budget accuracy, long-term cost insights | Long lifecycle products, capital-intensive buys | Reveals hidden costs, supports risk management |
| Reverse Auctions | Medium: platform setup, supplier readiness | Medium: auction management, supplier training | Cost savings (5-25%), reduced cycle time | Standardized, well-specified purchases | Transparent bidding, increased supplier competition |
| Make vs. Buy Analysis | Medium-High: comprehensive cost and risk analysis | Medium-High: cross-functional inputs | Cost reduction (15-40%), strategic sourcing choice | Evaluate internal capabilities vs outsourcing | Focus on core competencies, operational flexibility |
| Global Sourcing & Low-Cost Country Sourcing | High: complex logistics, risk management | High: audits, compliance, supply chain mgmt | High cost savings (20-60%), market expansion | Accessing low-cost suppliers, global market reach | Cost arbitrage, technology access, competitive alternatives |
Building a Future-Proof Procurement Powerhouse
The journey to optimizing procurement is not a single, linear path but a dynamic and continuous process of refinement. Throughout this guide, we've explored a powerful arsenal of seven distinct yet interconnected procurement cost savings strategies. From the foundational discipline of Strategic Sourcing to the data-driven precision of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis, each method offers a unique lever to pull in your quest for greater efficiency and value.
Moving beyond simple price negotiations is the central theme. Embracing e-procurement and automation frees your team from tactical busywork, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives. Similarly, consolidating suppliers and conducting rigorous make-or-buy analyses create economies of scale and streamline operations, directly impacting your bottom line. Meanwhile, tools like reverse auctions and the expansive opportunities of global sourcing open new avenues for competitive advantage that might otherwise remain undiscovered. The true power, however, lies not in deploying one of these tactics in isolation but in weaving them together into a cohesive, organization-wide philosophy.
Synthesizing Strategy for Maximum Impact
Think of these strategies as building blocks for a resilient, future-proof procurement function. A tech startup might prioritize automation and TCO analysis for its critical software stack, while a large Fortune 100 manufacturer could achieve massive wins through supplier consolidation and low-cost country sourcing for raw materials. The key is to map these strategies to your specific business context, risk tolerance, and long-term goals.
A world-class procurement team does far more than just cut costs; it acts as a central nervous system for the business. It mitigates supply chain risks, drives innovation by collaborating with cutting-edge suppliers, and enhances brand reputation through ethical sourcing. By mastering these approaches, you transform procurement from a transactional cost center into a strategic value-creation engine that directly contributes to competitive differentiation and sustainable growth.
Your Actionable Roadmap to Procurement Excellence
Implementing lasting change can feel daunting, so it's crucial to start with a focused, manageable plan. Do not attempt to overhaul everything at once. Instead, build momentum through a series of calculated wins.
Here are your immediate next steps:
- Conduct a Spend Analysis: Your first move is to understand where your money is going. Use data to identify the top 5-10 categories of spend. This is your treasure map, highlighting the areas with the most significant potential for savings.
- Identify a Pilot Project: Choose one or two high-impact, low-complexity categories from your analysis. Perhaps it’s consolidating office supplies or applying TCO analysis to your corporate travel program. A successful pilot will build confidence and secure buy-in for broader initiatives.
- Assemble a Cross-Functional Team: Involve stakeholders from finance, IT, marketing, and operations early and often. Their insights are invaluable, and their support is critical for smooth implementation. For example, a marketing team's input is essential when sourcing high-value promotional items or corporate gifts.
- Measure and Communicate Success: Define clear key performance indicators (KPIs) before you begin. Track savings, efficiency gains, and risk reduction. Share these results widely to demonstrate the value of strategic procurement and build support for future projects.
Ultimately, the most effective procurement cost savings strategies are those that are deeply embedded in your organization's culture. It’s about fostering an environment where every purchasing decision is viewed through a strategic lens, balancing cost, quality, risk, and long-term value. By taking these deliberate steps, you will not only achieve significant cost reductions but also build an agile, intelligent, and powerful procurement function that is ready for the challenges of tomorrow.
Ready to apply these strategies to one of your most visible spend categories? For corporate gifts and employee recognition programs, partnering with a specialist like Electronic Finishing Solutions streamlines procurement, eliminates hidden costs through all-inclusive pricing, and provides direct access to premium brands like Apple and Bose. See how our direct fulfillment model can simplify your process and maximize value by visiting Electronic Finishing Solutions today.



